Using git
Creating a repository locally (Optional)
If you were not able to create a GitHub repository and clone it locally (described in Section 2.2), before you proceed, you will need to create a local git repository. You can do that by using the following commands:
mkdir my_repo
cd my_repo
git init
Creating and Committing Files
First, let's makes a file.
echo "hello world" > hello.txt
We now have the hello.txt file containing "hello world." Because we have not yet committed this file, it is in the "untracked" state (underneath the "modified" / "working directory" state described in Section 2).
You can check this by running git's status command.
$ git status
On branch main
No commits yet
Untracked files:
(use "git add <file>..." to include in what will be committed)
hello.txt
nothing added to commit but untracked files present (use "git add" to track)
You can also see this using the git panel in VS Code.
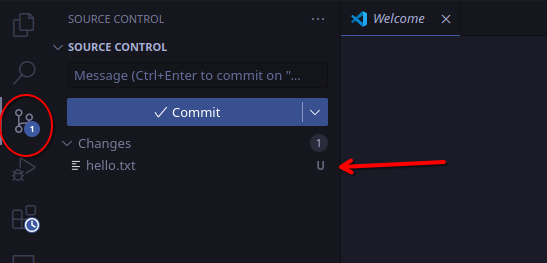
Before we commit this file, we need to add it to staging.
git add hello.txt
Alternatively, you can add all changes to staging using this command:
git add . # "." refers to the current directory
This process allows you to choose which files are included in each commit (instead of automatically adding all modified files to the current commit).
Let's check git's status again.
$ git status
On branch main
No commits yet
Changes to be committed:
(use "git rm --cached <file>..." to unstage)
new file: hello.txt
Next, let's make our commit.
git commit -m "My first commit!" # -m specifies the commit message
TIP: For commit messages do you not use past tense, such as "I made headings blue". Use language like "Make headings blue", as if you are giving orders to the codebase.
Here are a few other commit examples.
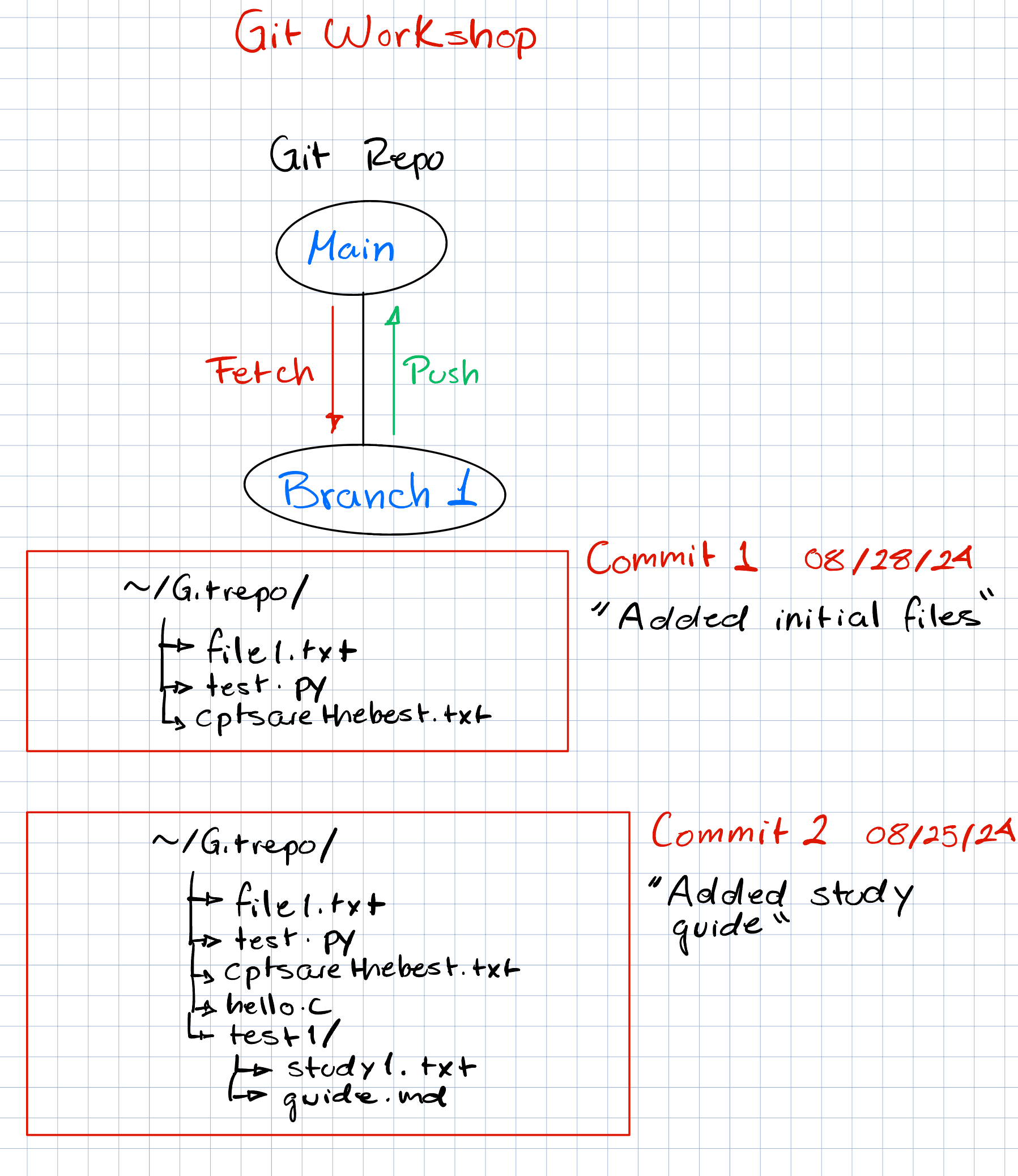
The commits of a project (including multiple branches) can be organized into a "commit tree", which looks something like this:
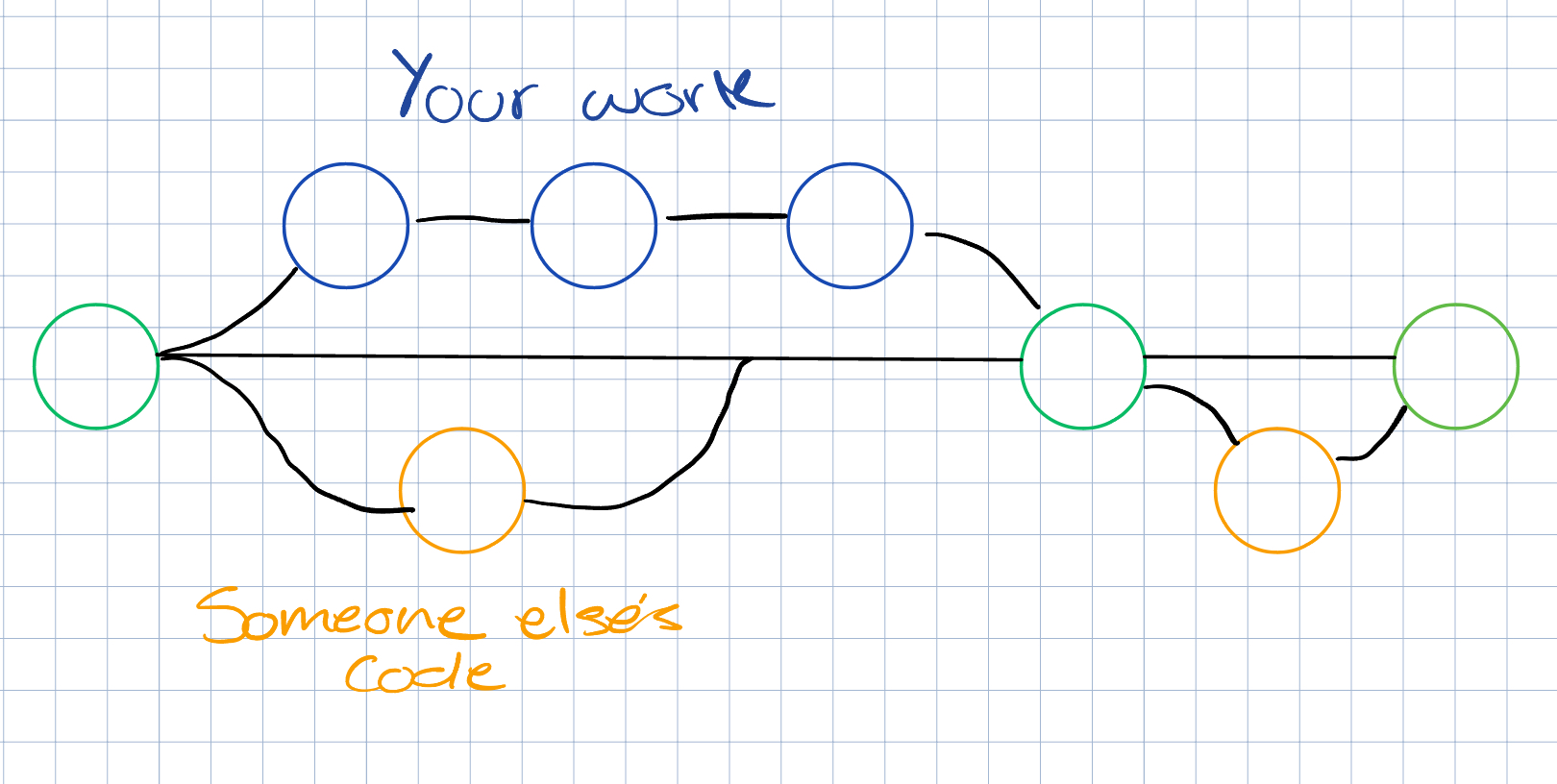
Branches
Branches allow you to work on different versions of your project simultaneously without affecting the main codebase
From this main code you can create branches, this allows you to make changes without the chance of ruining the main code. Think of it as a copy of your code that you can now change with zero risks.
Creating a Branch
Let's create a new branch using this command:
git checkout -b user/feature-a
You should now be on the user/feature-a branch. You can check this by running the git branch command.
Next, let's add a change to this branch
echo "foo bar" > foo.txt
git add .
git commit -m "Add foo.txt"
Let's go back to the main branch.
git checkout main
Note that the foo.txt file is no longer present.
$ ls
hello.txt
Merging Branches
To update the main branch with the changes from user/feature-a, run this command.
$ git merge user/feature-a
Updating f365571..0d24068
Fast-forward
foo.txt | 1 +
1 file changed, 1 insertion(+)
create mode 100644 foo.txt
If the files modified in main and user/feature-a (after user/feature-a was created or after the last merge) are mutually exclusive, then git should be able to do this automatically. However, if the same file was modified in both branches, you will encounter a merge conflict. Let's test this.
First, we'll make a change on the main branch.
echo "Hello CSU" >> hello.txt # >> appends to an existing file
git add .
git commit -m "Update hello.txt"
Next, let's make a change on the user/feature-a branch without updating (merging) the new changes on main.
echo "Hello engineering students!" >> hello.txt
git add .
git commit -m "Update hello.txt 2"
Now let's try to merge this.
$ git checkout main
$ git merge user/feature-a
Auto-merging hello.txt
CONFLICT (content): Merge conflict in hello.txt
Automatic merge failed; fix conflicts and then commit the result.
Before you do anything else, you will need to fix the merge conflicts. Git represents these conflicts within each file using the following format
# hello.txt
hello world
<<<<<<< HEAD
Hello CSU
=======
Hello engineering students!
>>>>>>> user/feature-a
To resolve this, replace the text above with the final desired version (it could be one or the other, or a combination of both). Once you've resolved all of the conflicts in (and saved) each file, stage the files and create a new commit. This completes the merge process.
For example, edit hello.txt like this:
# hello.txt
hello world
Hello CSU
Hello engineering students
Then run these commands:
git add .
git commit -m "Merge feature-a into main"
Note: you can also use git commit without a commit message. It will then open an editor for you the write the commit message. once you save the message and exit the editor, git will make the commit.
Afterwards, you may delete user/feature-a.
git branch -d user/feature-a
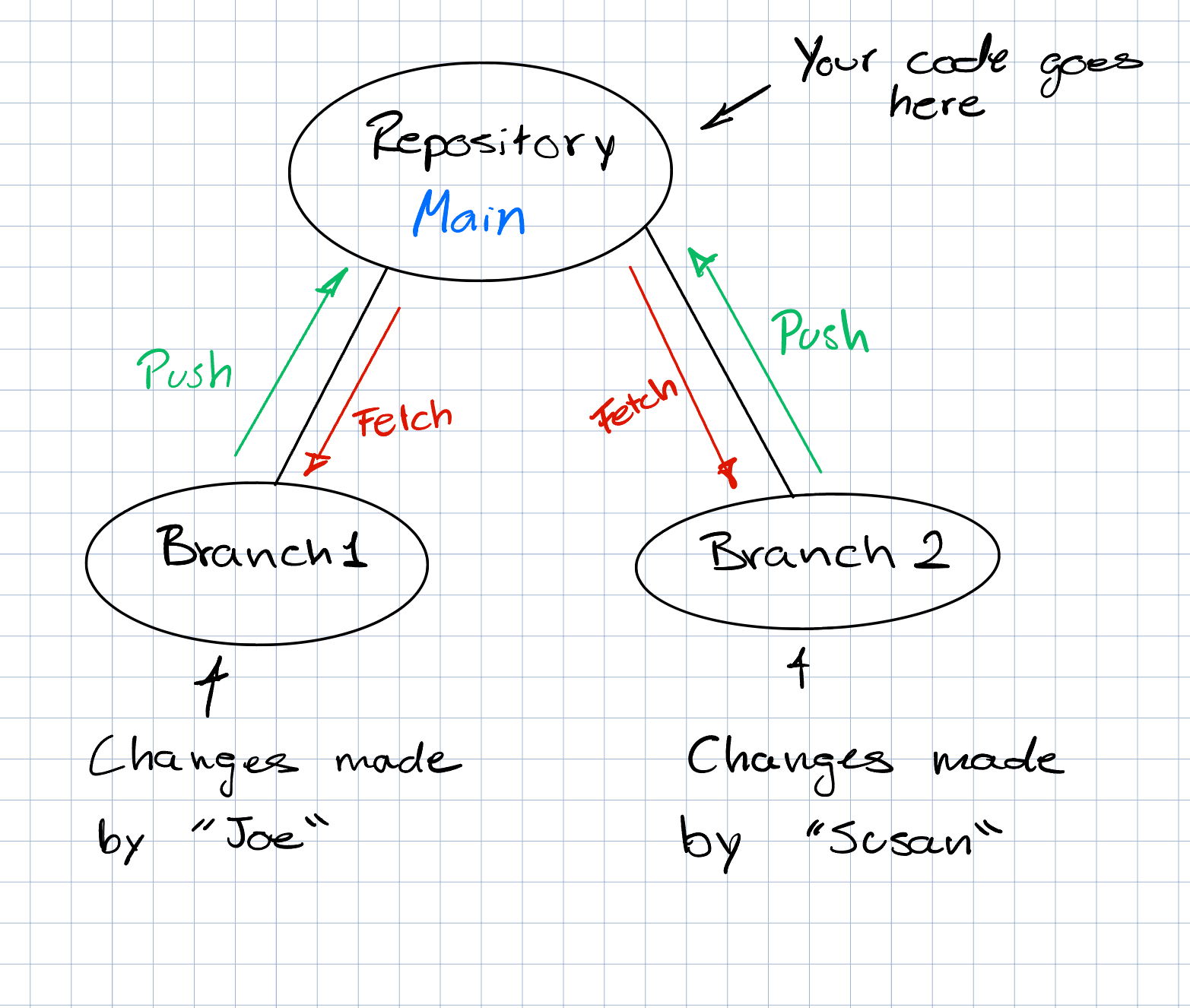
Remotes
First, make sure that you've created your repo through GitHub (see Section 2.2). Alternatively, you can create another GitHub repo (with no files) and then add it as a remote to your current repo.
Use the URL of the blank GitHub repository to set it as the remote destination for your local git-tracked repository:
git remote add origin <GitHub_Repository_URL>
Now, push your local commits to the main branch on GitHub, setting the upstream tracking reference.
git push -u origin main
Merging branches and Pull Requests
This is how you create a Pull Request for your branch on GitHub:
- On GitHub, navigate to the main page of the repository.
- In the "Branch" menu, choose the branch that contains your commits.
- Above the list of files, in the yellow banner, click Compare & pull request to create a pull request for the associated branch.
- Use the base branch dropdown menu to select the branch you'd like to merge your changes into, then use the compare branch drop-down menu to choose the topic branch you made your changes in.
- Type a title and description for your pull request.
- To create a pull request that is ready for review, click Create Pull Request.
Troubleshooting: Merging with remote branches
From github.com:gaverkov/mixed_volumes_proposal
* branch main -> FETCH_HEA
hint: You have divergent branches and need to specify how to reconcile them.
hint: You can do so by running one of the following commands sometime before
hint: your next pull:
hint:
hint: git config pull.rebase false # merge
hint: git config pull.rebase true # rebase
hint: git config pull.ff only # fast-forward only
hint:
hint: You can replace "git config" with "git config --global" to set a default
hint: preference for all repositories. You can also pass --rebase, --no-rebase,
hint: or --ff-only on the command line to override the configured default per
hint: invocation.
VS Code Git Integration
Visual Studio Code has integrated source control management (SCM) and includes Git support out-of-the-box. Here are a few good resources to reference on how to use it:
-
https://code.visualstudio.com/docs/sourcecontrol/overview
-
https://www.gitkraken.com/blog/vs-code-git
Git Best Practices
-
Commit Often: Make small, frequent commits to capture your progress.
-
Write Clear Commit Messages: Use descriptive messages that explain why a change was made, not just what changed.
-
Use Branches: Create branches for features, fixes, and experiments to keep your main branch stable.
-
Pull Before You Push: Always
git pullbefore pushing. -
Review Changes Before Committing: Use
git statusandgit diffto review your changes before you commit. -
Keep Repositories Small: Avoid adding large files or unnecessary dependencies.
-
Use .gitignore: Exclude files that shouldn't be tracked (like build artifacts, log files, or secrets) by adding them to a
.gitignorefile.
https://www.w3schools.com/git/git_best_practices.asp